What Is a VPN and How Does It Work? A Simple Explanation for Beginners (2025)
By Your Name • Updated: • Read time: ~13–15 minutes
What is a VPN and how does it work? In this beginner-friendly guide for 2025 we’ll explain the concept in plain English, show how VPNs protect your connection, highlight common uses (streaming, privacy, remote work), describe protocols and encryption, and give practical tips for choosing and using a VPN safely.
Simple explanation — the short version
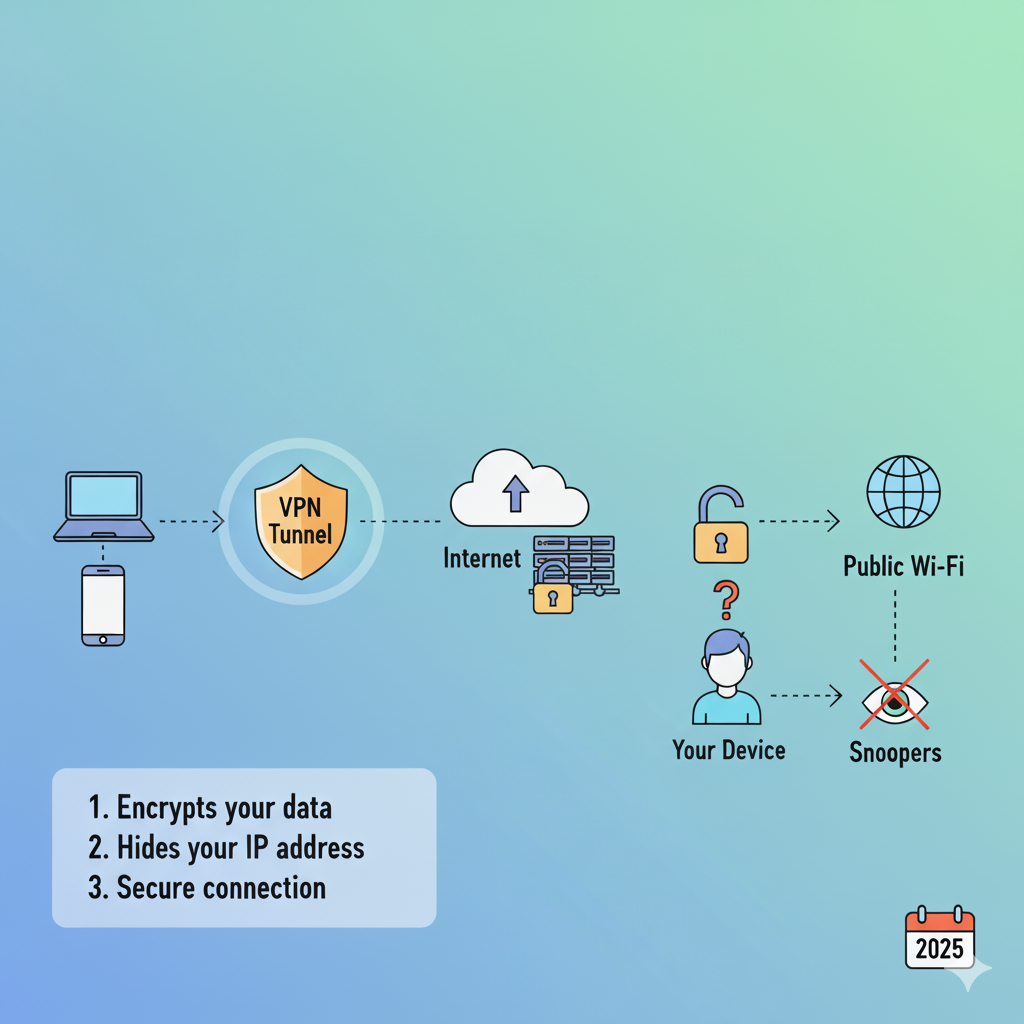
A VPN (Virtual Private Network) lets you create a secure, encrypted connection between your device and a remote server operated by the VPN provider. Think of it as a private tunnel through the internet: data that travels through that tunnel is encrypted and hides your real location and IP address from websites, networks, and onlookers.
Analogy: Imagine sending a letter. Without a VPN, you put the letter in a normal envelope and anyone who handles it can peek. With a VPN, you put the letter in a tamper-proof locked box that only you and the recipient can open — even the postal workers can’t read it.
How a VPN works — step by step
Here’s a simplified sequence of what happens when you use a VPN.
- You open the VPN app on your device and connect to a server (for example, in another country or your own country).
- Your device and the VPN server establish an encrypted connection using a VPN protocol (examples below). That connection is the “tunnel.”
- Your internet traffic is routed through the VPN server — websites and services see the VPN server’s IP address (not your real IP).
- Data between your device and the VPN is encrypted, so your ISP, public Wi‑Fi providers, and network attackers can’t read it.
- The VPN server forwards your requests to websites and then sends the responses back through the encrypted tunnel to your device.
In short: your device ↔ encrypted tunnel ↔ VPN server ↔ destination website. The VPN server acts as an intermediary that hides your identity and secures your data in transit.
Encryption & VPN protocols — explained simply
Two concepts matter most: encryption and protocols.
Encryption
Encryption scrambles your data so only someone with the correct key can read it. Modern VPNs use strong encryption (AES-256 is common) which is extremely hard to break. That means even if someone intercepts your traffic, they can’t decipher it without the key.
VPN protocols
A protocol is the set of rules that create and manage the VPN connection. Popular protocols in 2025 include:
- WireGuard — Fast, modern, and simple; widely adopted for its performance.
- OpenVPN — Battle-tested and flexible; supported on many platforms.
- IKEv2/IPsec — Reliable, especially on mobile devices that switch networks frequently.
- Proprietary protocols (e.g., Lightway, NordLynx) — Custom protocols tuned for performance by specific providers.
For most users in 2025, WireGuard (or provider equivalents like NordLynx) offers the best mix of speed and security. But OpenVPN still has advantages for advanced configurations and obscure networks.
Common VPN use cases in 2025
People use VPNs for many reasons. Here are the most common, with beginner-friendly examples:
1. Secure public Wi‑Fi
When you connect to coffee‑shop Wi‑Fi, attackers on the same network can try to intercept data. A VPN encrypts your connection so those attackers can’t read your traffic.
2. Privacy from your ISP and advertisers
Your Internet Service Provider (ISP) can see the sites you visit. A VPN hides your traffic from the ISP (though the VPN provider can see it — more on trust below).
3. Bypass geo-restrictions
Streaming services and websites sometimes block content by country. Connecting to a VPN server in a different country can let you access region-locked content.
4. Safer remote work
Many companies require remote employees to use a VPN to access internal resources securely.
5. P2P and torrenting
Some users route torrenting traffic through VPNs to hide their IP addresses from peers. Choose a provider that allows P2P and has a clear no-logs policy.
Pros & cons — what a VPN can and cannot do
What a VPN can do
- Encrypt your internet traffic between your device and the VPN server.
- Hide your real IP address from websites and networks.
- Reduce certain types of tracking and profiling based on IP.
- Help bypass simple geo-blocks for streaming or websites.
What a VPN cannot do
- Make you completely anonymous — the VPN provider can still see your traffic unless you use additional privacy measures.
- Protect against phishing websites or malware on your device — use antivirus and safe browsing habits.
- Fix insecure websites — a VPN does not make an unencrypted HTTP site secure.
- Ensure legal protection — using a VPN does not make illegal activities legal.
Trust & privacy: who can see your data?
Important: a VPN moves the point of trust from your ISP to the VPN provider. When you use a VPN:
- Your ISP sees an encrypted connection to the VPN server but not the websites you visit.
- The VPN provider can see (and potentially log) your activity unless they have a strict no‑logs policy and independent audits to prove it.
- Some providers operate under jurisdictions that can be more or less privacy-friendly — this affects legal obligations to disclose data.
Pick VPNs that publish transparent privacy policies, undergo independent audits, and ideally support privacy-friendly jurisdictions. If ultimate privacy is required, combine a VPN with other tools (Tor, secure email, privacy-focused OS) and always follow best practices.
How to choose a VPN in 2025
Use this quick checklist when comparing providers:
- No-logs policy: Prefer providers with audited no‑logs claims.
- Protocols: Look for WireGuard or strong alternatives.
- Server network: More servers and countries give flexibility for speed and unblocking.
- Speed & performance: Check independent speed tests and real-world reviews.
- Streaming & P2P: If you need these, confirm provider support and server labels.
- Simultaneous connections: Make sure you can protect all your devices.
- Refunds & trials: Short-term trials or money-back guarantees let you test performance from your location.
Quick setup & safety tips
- Download the official app from the provider’s website or your device store.
- Enable the kill switch (if available) to prevent leaks when the VPN disconnects.
- Use strong, unique passwords and enable multi-factor authentication (MFA) on your VPN account.
- Test for IP/DNS/WebRTC leaks using reputable online tools after setup.
- Combine VPN use with browser privacy settings and an ad/tracker blocker for better privacy.
# Example: connect to a VPN with WireGuard on Linux (simplified) # Install wireguard tools and import the config file provided by your VPN sudo apt update && sudo apt install wireguard -y sudo wg-quick up wg0.conf
FAQs — quick answers
Is a VPN legal?
In most countries, yes. Some countries restrict or ban VPN use; always check local laws.
Will a VPN slow down my internet?
Possibly. Encryption and routing add overhead, but modern providers and protocols minimize the impact—especially with WireGuard.
Can I use a free VPN?
Free VPNs exist, but many have limits or weaker privacy. Some free providers are reputable (limited tiers). For heavy use or sensitive tasks, a reputable paid VPN is safer.
Which VPN protocol should I pick?
WireGuard is generally recommended in 2025 for speed and security, but OpenVPN and IKEv2 remain useful for compatibility.
Conclusion — is a VPN right for you?
A VPN is a powerful, easy-to-use tool for improving privacy and security on the internet, especially on public Wi‑Fi and for bypassing simple geo-restrictions. It’s not a silver bullet — you should pair it with good security habits and choose a reputable provider. For most beginners in 2025, a VPN using WireGuard from a trusted, audited provider offers the best balance of performance and privacy.
If you’d like, I can now recommend the top VPNs for your country and use-case, or produce a short comparison table of the best free vs paid options. Get personalized recommendations